electro-spinning
Electrospinning offers the possibility to produce nanofibers with diameters in the range from a few micrometres down to some 100 nanometres. At the LSP a variety of polymers and polymer blends from different solvent systems can be spun.
When electrospinning a polymer solution or polymer melt is pumped through a needle. When a high voltage source is attached to the needle or collector, the polymer fibers will be accelerated in the set electric field towards the collector. At the facilities of the LSP several electrospinning devices are available with alternating polarisation and different collector types. By adjusting different process parameters e.g. voltage, flow rate, needle-to-collector distance and the type of collector the resulting fibers can be influenced regarding morphology, alignment and structure.
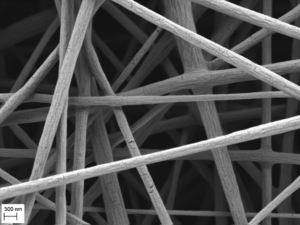
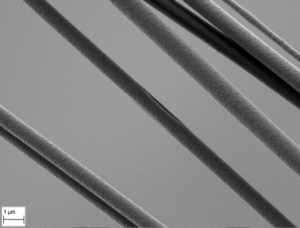
With a simple plate collector, nanofiber membranes with a random distribution of fiber orientation can be produced. For aligned structures the LSP provides two different setups: a parallel bar collector and a rotating drum collector. With the rotating drum collector the fiber yield can be maximised and in addition a further optimisation of the fibers can be achieved by varying the rotation speed.
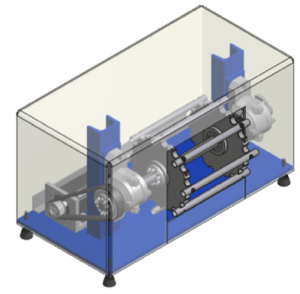
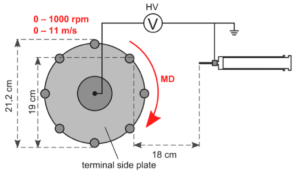
For most applications of nanofibers the fiber diameter is of crucial importance. Based on a purely physical consideration of the electrospinning process by Schubert (Macromolecular Theory and Simulations 28 (2019)) a theoretical prediction of the fiber diameter distribution can be made. The corresponding code to the paper can be found here.
